For Hassana in Kogi, Nigeria, October’s floods were not like years past. “All our farmlands washed away as many had not yet harvested what they planted. The flooding continued until our homes and other things were destroyed. At this point we were running helter-skelter,” she said.
These floods, the worst in a decade, result from predictable seasonal rains. If we can anticipate floods, we can also anticipate the action needed to help. So why does aid often take months (even up to a year) to reach people like Hassana? Traditional humanitarian processes can be slow and cumbersome, government and aid agencies often lack the capacity and money to respond, and most aid is delivered in person, an added challenge when infrastructure is damaged.
Digital cash transfers can avoid these issues, and getting them to work in a disaster setting means more people will survive climate change. In the past year, with support from Google.org, GiveDirectly ran pilots to send cash remotely to flood survivors: in Nigeria, we sent funds to survivors weeks after flooding and in Mozambique, we sent funds days before predicted floods. Below, we outline what worked, what didn’t, and how you can help for next time.

Over 1.5B people in low and middle income countries are threatened by extreme floods. Evidence shows giving them unconditional cash during a crisis lets them meet their immediate needs and rebuild their lives. However, operating in countries with limited infrastructure during severe weather events is complicated, so we ran two pilots to test and learn (see Appendix):

What went right and what went wrong
Innovating in the face of climate change requires a ‘no regrets’ strategy, accepting a degree of uncertainty in order to act early to prevent suffering. In that spirit, we’re laying out what worked and did not:
✅ Designing with community input meant our program worked better
A cash program only works if recipients can easily access the money. In Nigeria, we customized our program design based on dozens of community member interviews:
- 👂Use the local dialect: There are 500+ dialects spoken in Nigeria, and our interviews determined a relatively uncommon one, Egbura Koto, was most widely used in the villages we were targeting. We hired field staff who spoke Egbura Koto, which made the program easier to access and more credible to community members, with one saying, “I didn’t believe the program at first when my husband told me but when I got a call from GiveDirectly and someone spoke in my language, I started believing.”
- 📱Promote mobile money: Only 10% of Nigerians have a mobile money account (compared to 90% of Kenya), so we planned to text recipients instructions to create one and provide a hotline for assistance. But would they struggle to set up the new technology? Our interviews found most households had at least one technologically savvy member, and younger residents often helped their older or less literate neighbors read texts, so we proceeded with our design. In the end, 94% of surveyed recipients found the mobile money cash out process “easy.”
- 💵 Send cash promptly: Cash is most useful where markets are functioning, so should we delay sending payments until floods recede if it means more shops will be reopened? In our interviews, residents explained the nearby Lokoja and Koton-Karfe markets functioned throughout flooding and could be reached in 10 minutes by boat. We decided not to design in a delay and found the nearby markets were, in fact, open during peak flooding.

❌ We didn’t send payments before severe floods
In Mozambique, we attempted to pay people days ahead of severe floods based on data from Google Research’s Flood Forecasting Initiative, using a model validated on the only available data source: 50 years of government river level measurements. During Cyclone Freddy’s second landfall, our forecasts predicted river levels would rise to dangerous levels in the region, so we sent anticipatory $225 transfers to 4,183 people across 11 villages, aiming to help families prepare.
Ultimately, severe floods never came in the villages we paid, though some un-enrolled villages in nearby areas were flooded as Cyclone Freddy was the most significant of the season. Though we couldn’t respond in villages hit the hardest, we still paid people who are consistently vulnerable to climate disasters: 90% of people who received this payment had survived a significant flood in the prior year.
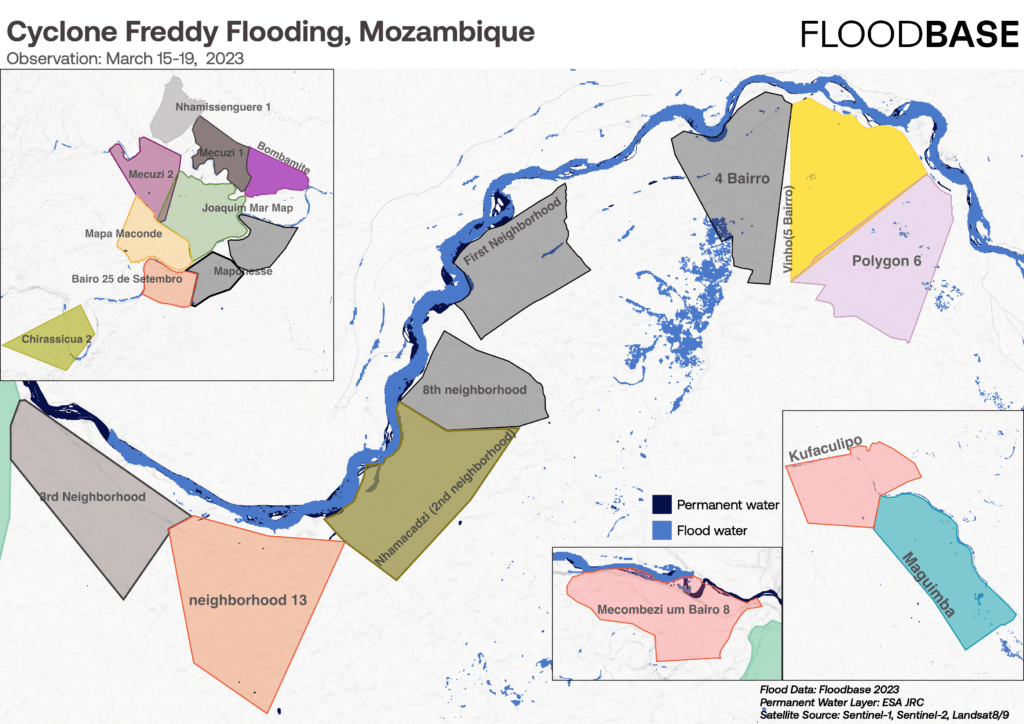
In the future, we need more flexibility on where to respond and to incorporate more than one trigger from forecasts to make sure we respond at the right time and where floods are most severe. In addition to overflowing rivers, floods are also caused by rain (flash floods), which are hard to predict on a village level, and certain villages are more likely to flood than their neighbors due to subtle geographic differences. In post-pilot conversations, these communities also told us they’d need payments more than several days ahead of a flood event to fully utilize the cash and prepare.
As we scale up anticipatory action, we’ll continue working with Google Research, local communities, and experts to:
- Factor in more predictors to better weigh overall probability of a major flood event, and ensure we respond in advance
- Integrate local data to further optimize our triggers for different regions, such as by learning more from communities’ past experiences with floods
- Target a larger area to ensure we have more flexibility to respond in whichever villages are most at risk for the type of impending flood
- Send payments even earlier, 4-5 days before a major flood event, so people have more time to prepare
❌ Limited pre-enrollment meant we lacked flexibility to respond to the worst floods
When Cyclone Freddy approached Mozambique, we could tell it would likely hit hardest far north of where we’d pre-enrolled villages – but we couldn’t pivot and pay the villages that were clearly about to experience the worst floods. Though we had more luck in Nigeria predicting where floods would hit, we accepted some uncertainty with our village selection. This lack of flexibility was a major limitation, but our budget limited us to only pre-enrolling a relatively small area.
A larger potential payment area means a more responsive program. There are two ways we can improve, each with its own trade-off:
- Remotely enroll and pay based on storm path, excluding people without phones: We could use real-time mobile phone data or disaster registries to contact people in a storm’s path, enrolling and paying them fully remotely. This would give us more geographic flexibility for a lower cost, but we’d only reach people who already use mobile phones. Fewer than 40-60% of rural Mozambique has a SIM card, so this would likely mean excluding the poorest half of impacted families.
- Manually pre-enroll more villages, reaching fewer people: In our Mozambique pilot, we held in-person SIM card and mobile money registration drives to reduce how many people were excluded. However, scaling this up to pre-enroll a larger area would require hiring more staff, reducing the overall program efficiency and therefore reaching fewer people.

✅ Ultimately, people in poverty affected by floods got money
One reason for our ‘no regrets’ principle is that any money put in the hands of people in extreme poverty is a good thing. Nearly all of the families in Mozambique paid ahead of March’s forecasted river floods that never came had suffered from other flooding in the prior year and used the funds to improve their resilience. Across both countries, we delivered $3M to 13,782 families impacted by both flooding and poverty, which they spent on things like agricultural inputs to restore damaged cropland, evacuation to safer areas, food and essential goods, and home repairs/improvements (see Appendix)
Without your support, we cannot try again
Our Google.org-funded pilots prove it’s possible to quickly send cash aid to flood survivors in extreme poverty. We already have actionable ways to improve our flexibility, accuracy, and speed next time. But in typical humanitarian grantmaking, funding is only released after a flood happens, which leaves little room to innovate. We need more donors committed to giving funds for climate survivors before the crisis hits.
As the New York Times observed, bringing our work to scale could change how billions of dollars in loss and damage climate funding is spent. What works for 10,000 people could soon reach millions.
Appendix 1 – Program design
We identified the most vulnerable villages using 3 types of data
We selected communities at high risk of devastation from floods before storm season by layering historical flood data (from our partners Floodbase and Fathom), granular poverty maps, and crops and village density derived from satellite imagery. We then visited some of these areas to consult local authorities, validate our map predictions, and determine which were the poorest and most at risk of flooding. In just 3 weeks, we narrowed in on four wards in Kogi State, Nigeria and parts of Nhamatanda district, Mozambique to target.
We pre-enrolled 87 villages for relief ahead of flooding
Our teams then pre-enrolled 65 villages in Nigeria and 22 in Mozambique, hosting village-wide meetings to raise awareness of the pilot, and in some cases distributing SIM cards and running mobile money registration drives. For recipients, actually enrolling took just a few minutes – once they completed a short mobile phone survey, our systems verified their information through telecom, ID, and government databases[1].
We triggered payments just before or upon flooding
In Nigeria, we enrolled people in mid-September 2022 (just before the peak of the flood season) so that we could send payments to 6k families as soon as a major flood began. In Mozambique, we aimed to pay people before floods hit, so as Cyclone Freddy made a second landfall in March 2023, we sent 4k families payments 3 days ahead of when flood forecasting models predicted rivers would rise significantly in our target areas. We also paid another 3.6k families a month after predicted flooding.
Appendix 2 – Recipient impact and spending
[1] In the case of Nigeria, we used the National Social Register database (under the Government’s National Social Safety Net Coordinating Office (NASSCO)). Where we found gaps in available data, our teams conducted in-person checks or contacted people via our call center.